
Shuning Sun
Biography
Hello! I am a M.S. student at Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. I obtained my B.E. in Mathematics and Applied Mathematics at Shenyang University of Technology in 2023.
My research interests lie in the intersection of Computer Vision and AICG.
From 2023, I started to do research on image/video restoration.
Now, I focus on designing novel applications for image/video restoration and AIGC tasks.
I am also passionate about crypto and Web3, having developed several innovative projects in this domain.
📧 Feel free to contact me by email if you are interested in discussing or collaborating with me.
🔥 News
- [01/2026] One paper accepted by ICLR 2026 🎉 🎉 🎉
- [10/2025] Two papers accepted by AAAI 2026 🎉 🎉 🎉
- [10/2025] Got National Scholarship for Graduate Students 🎉 🎉 🎉
Industrial Experience

|
VIVO Sep. 2025 - Dec. 2025 VIVO Imaging Algorithm Research Center, Hangzhou, China Topic: Light and Shadow Portrait Large Model Algorithm Research |

|
Hyperchain Aug. 2023 - Sep. 2025 Hyperchain Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China Topic: Blockchain and Quantitative Trading |
Education & Visiting

|
Zhejiang University, China Visiting Student in Computer Science May. 2025 - Sep. 2025 |

|
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Master of Science in Computer Technology Sep. 2023 - Present |

|
Shenyang University of Technology, China Bachelor of Engineering in Mathematics and Applied Mathematics Sep. 2019 - Jun. 2023 |
Selected Publications · [Full List →]
Preprints
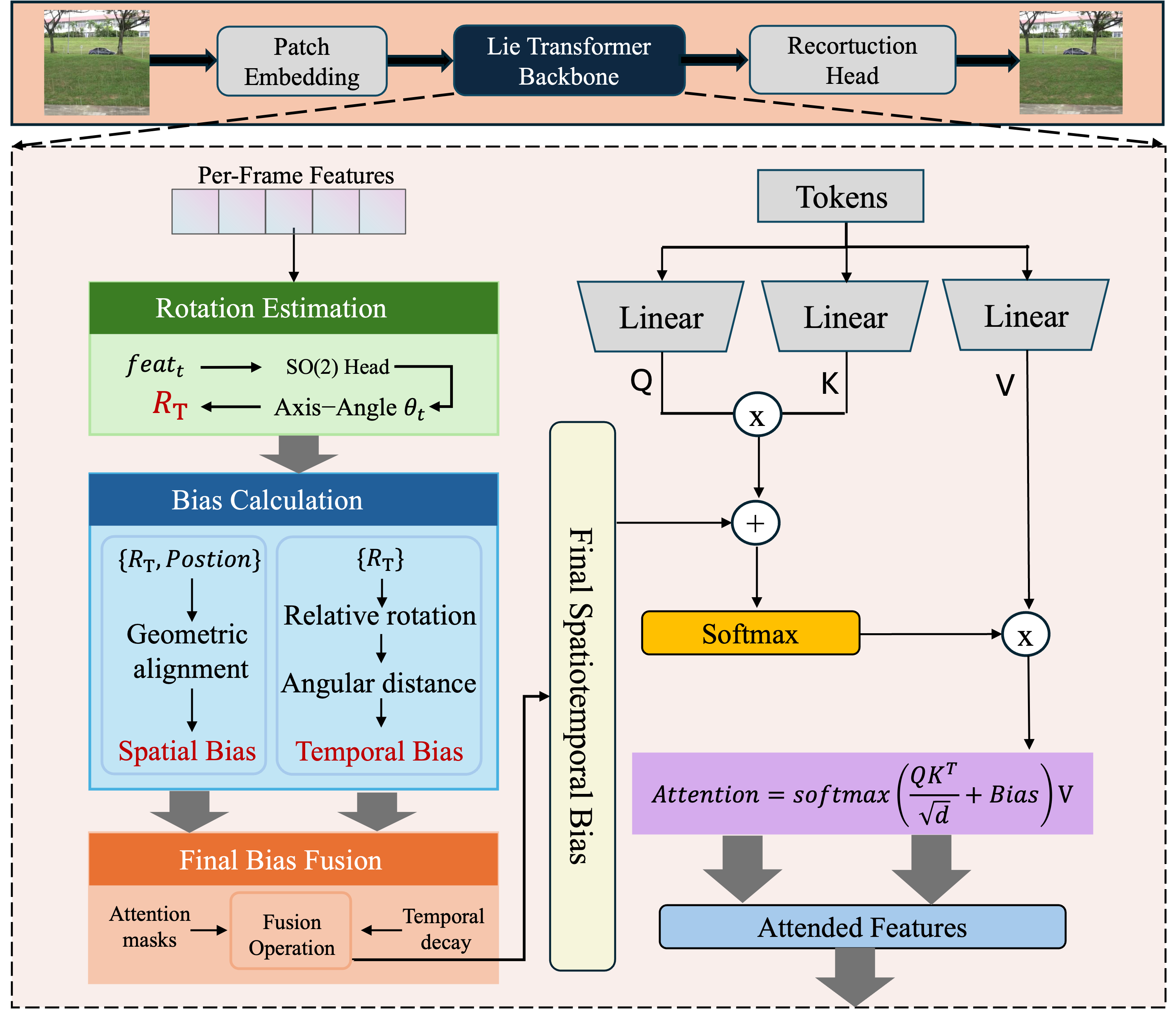
|
DeLiVR: Differential Spatiotemporal Lie Bias for Efficient Video Deraining Shuning Sun, Jialang Lu, Xiang Chen, et al. Submitted Paper |
Conferences
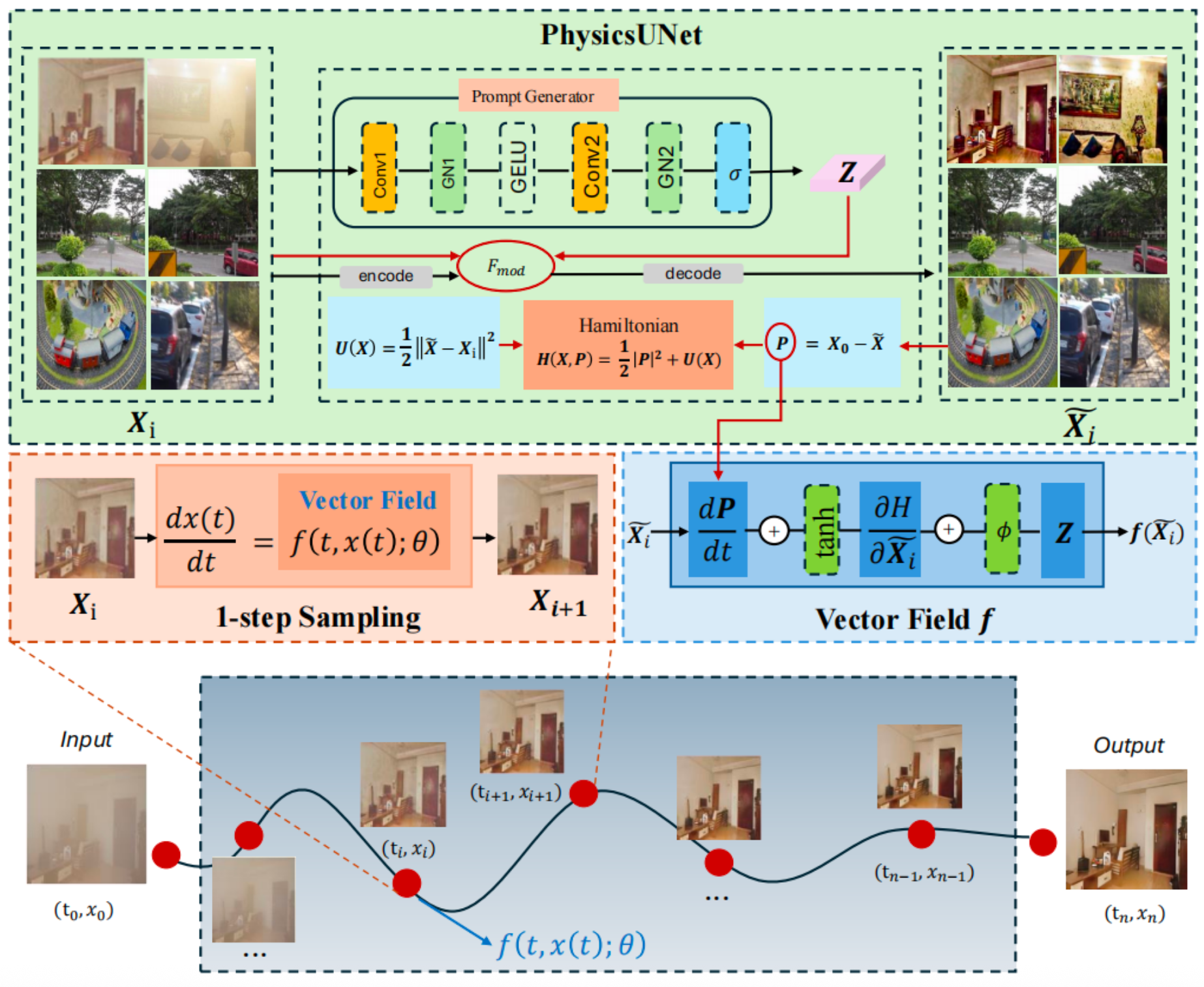
|
UniFlowRestore: A General Video Restoration Framework via Flow Matching and Prompt Guidance Shuning Sun, Yu Zhang, Chen Wu, et al. Accepted by ACM MM 2026 Paper |
Honors & Awards
[10/2025]
National Scholarship for Graduate Students.
[04/2024]
Web3.0 Innovation Competition — RentChain, Third Prize in Hong Kong Region.
[08/2021]
China Computer Games Competition — Connect Six AI, National Second Prize.
[09/2021]
Mathematical Contest in Modeling — Second Prize, Liaoning Province.
© Shuning Sun